Decision Tree
example
| Color | Diameter | Label |
|---|---|---|
| Green | 3 | Apple |
| Yellow | 3 | Apple |
| Red | 1 | Grape |
| Red | 1 | Grape |
| Yellow | 3 | Lemon |
Difficulties: No visual way to seperate features since sample 2 and sample 5 share the same features while having different labels
Family of Decision Tree Learning Algorithms:
- ID3
- C4.5
- C5.0
- CART
CART
CART stands for classification and regression trees
CART overview:
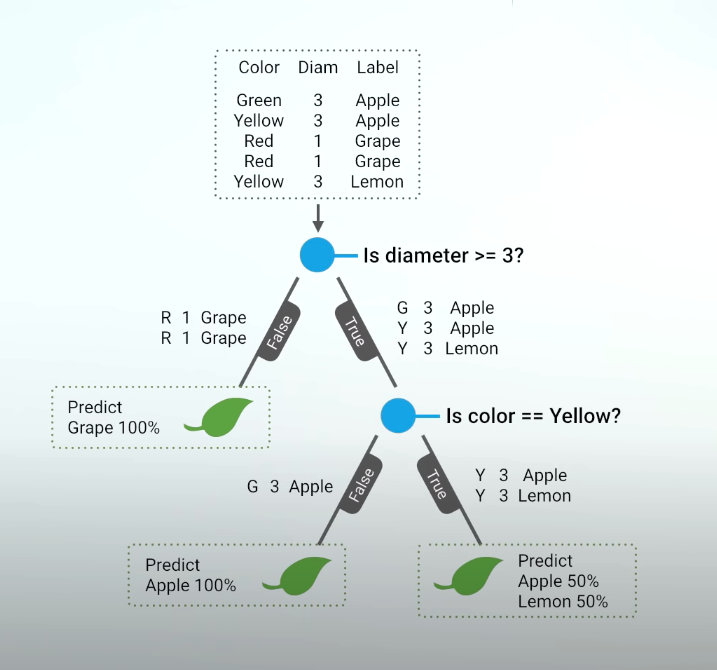
The trick to build an effective tree is to understand which questions to ask and when. And to do that, we need to quantify how much a question helps to unmix the labels. And we can quantify the amount of uncertainty at a single node using a metrix called Gini impurity. And we can quantify how much a question reduces that uncertainty using a concept called information gain.
import modules
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
training data in our test example
training_data=[
['Green',3,'Apple'],
['Yellow',3,'Apple'],
['Red',1,'Grape'],
['Red',1,'Grape'],
['Yellow',3,'Lemon'],
]
print(training_data)
[['Green', 3, 'Apple'], ['Yellow', 3, 'Apple'], ['Red', 1, 'Grape'], ['Red', 1, 'Grape'], ['Yellow', 3, 'Lemon']]
transform categorical data into integers:
def encode_data(training_data):
n_features = len(training_data[0])
data_set = []
for col in range(n_features):
x = [ data[col] for data in training_data ]
if isinstance(training_data[0][col],int):
data_set.append(x)
continue
y = label_encoder.fit_transform(x)
temp = y.tolist()
data_set.append(temp)
arr = np.array(data_set)
arr = arr.T
data_set = arr.tolist()
return data_set
data_set = encode_data(training_data)
data_set
[[0, 3, 0], [2, 3, 0], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [2, 3, 2]]
question class

class Question:
# a question is used to partition a dataset
def __init__(self, column, value):
self.column = column
self.value = value
def match(self, example):
# compare the feature value in an example to the feature
# value in this quesiton
val = example[self.column]
return val >= self.value
## demo
# let's write a question for a numeric question
q=Question(1,3)
example = data_set[3]
q.match(example) #this will be false since forth example diameter is less than 3
False
partition function

def partition(rows, question):
#partitions dataset, rows: dataset question is used to seperate dataset into two different list
true_rows,false_rows=[],[]
for row in rows:
if question.match(row):
true_rows.append(row)
else:
false_rows.append(row)
return true_rows, false_rows
#demonstrate training data whether first categorical value is >=1
true_rows, false_rows = partition(data_set, Question(0,0))
true_rows, false_rows
([[0, 3, 0], [2, 3, 0], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [2, 3, 2]], [])
Gini Impurity
Chance of being incorrect if you randomly assign a label to an example in the same set. It is a measurement of the likelihood of an incorrect classification of a new instance of a random variable. Gini Impurity means all data contains only one class.
How to calculate gini impurity:
where p_instance(i) is the probablity to randomly select an instance, m is number of example/instances, n is number of class/labels, k is frequency of current instance, p(i) is the probability of an item with label i being chosen, which is also the fraction of items labeled with class i in the set.
reference regarding to Gini Impurity:
- https://victorzhou.com/blog/gini-impurity/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree_learning#Gini_impurity
def gini(rows):
# """ calculate the gini impurity for a list of rows"""
datasets = np.array(rows)
impurity = 1
if datasets.size == 0:
return 0
#number of labels
unique,counts=np.unique(datasets[:,-1],return_counts=True)
for label,count in zip(unique,counts):
prob = count / float(np.size(rows,0))
impurity -= prob**2
return impurity
gini(data_set)
0.6399999999999999
demo, a dataset with no mixing
no_mixing = [['Apple'],
['Apple']]
# this will return 0
gini(no_mixing)
0.0
demo, a dataset with many different labels
lots_of_mixing = [['Apple'],
['Orange'],
['Grape'],
['Grapefruit'],
['Blueberry']]
gini(lots_of_mixing)
0.7999999999999998
Information Gains
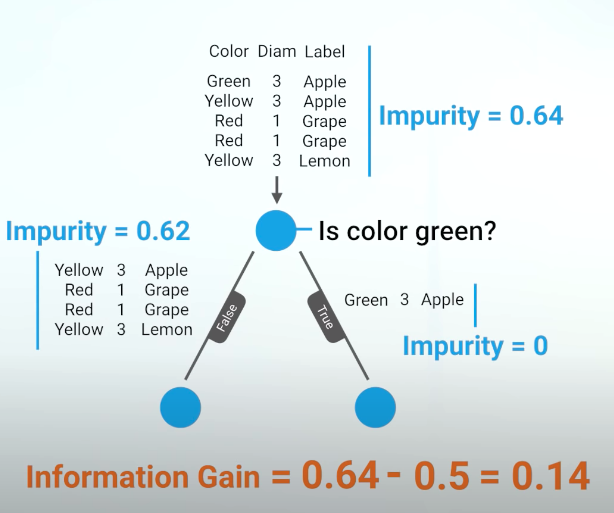
def info_gain(left, right, current_gini_impurity):
#the uncertainty of the starting node, minus the weighted impurity of two child nodes
p = float(len(left)) / (len(left) + len(right))
return current_gini_impurity - p * gini(left) - (1-p) * gini(right)
calculate the uncertainty of training data
current_impurity = gini(data_set)
current_impurity
0.6399999999999999
datasets = np.array(data_set)
# true_rows,false_rows = partition(data_set, Question(0,0))
# info_gain(true_rows,false_rows,current_impurity)
# datasets[0,1]
for data in datasets[:,1]:
# print(data)
true_rows,false_rows = partition(data_set, Question(1,data))
print(info_gain(true_rows,false_rows,current_impurity))
0.37333333333333324
0.37333333333333324
0.0
0.0
0.37333333333333324
build the tree using recursion
def find_best_split(rows):
#find the best question to ask by iterating over every feature/value and calculating the information gain
current_impurity = gini(rows)
best_gain = 0
best_question = None
n_features = len(rows[0])-1
datasets = np.array(data_set)
for col in range(n_features):
unique,counts=np.unique(datasets[:,col],return_counts=True)
for val,count in zip(unique,counts):
question = Question(col,val)
true_rows,false_rows = partition(rows,question)
gain = info_gain(true_rows, false_rows, current_impurity)
# print(col, val, gain)
if gain >= best_gain:
best_gain, best_question = gain, question
return best_gain, best_question
best_gain, best_question = find_best_split(data_set)
best_gain
0.37333333333333324
build tree
class Leaf:
def __init__(self, rows):
self.datasets = np.array(rows)
self.unique, self.counts = np.unique(self.datasets[:,-1], return_counts=True)
class Decision_Node:
def __init__(self,question,true_branch,false_branch):
self.question = question
self.true_branch = true_branch
self.false_branch = false_branch
def build_tree(rows):
gain, question = find_best_split(rows)
if gain == 0:
return Leaf(rows)
true_rows, false_rows = partition(rows, question)
true_branch = build_tree(true_rows)
false_branch = build_tree(false_rows)
return Decision_Node(question, true_branch, false_branch)
def print_tree(node):
if isinstance(node, Leaf):
print("leaf")
print((node.unique,node.counts))
return
print("question is: ")
print(node.question.column, node.question.value)
print ('--> True:')
print_tree(node.true_branch)
print ('--> false:')
print_tree(node.false_branch)
test = build_tree(data_set)
print_tree(test)
question is:
1 3
--> True:
question is:
0 2
--> True:
leaf
(array([0, 2]), array([1, 1]))
--> false:
leaf
(array([0]), array([1]))
--> false:
leaf
(array([1]), array([2]))
def classify(row, node):
if isinstance(node, Leaf):
return node.unique, node.counts
if node.question.match(row):
return classify(row, node.true_branch)
else:
return classify(row, node.false_branch)
classify(data_set[0],test)
(array([0]), array([1]))
testing_data = [
['Green', 3, 'Apple'],
['Yellow', 4, 'Apple'],
['Red', 2, 'Grape'],
['Red', 1, 'Grape'],
['Yellow', 3, 'Lemon'],
['Red', 2, 'Apple'],
['Yellow', 4, 'Apple'],
['Green', 5, 'Grape'],
['Yellow', 1, 'Grape'],
['Green', 3, 'Lemon'],
]
def encode_data(training_data):
label_encoder = LabelEncoder()
x_color= [ x[0] for x in training_data]
x_label= [ x[2] for x in training_data]
y_color = label_encoder.fit_transform(x_color)
y_label = label_encoder.fit_transform(x_label)
data_set=[ [col1,col2[1],col3] for (col1,col2,col3) in zip(y_color,training_data,y_label)]
return data_set
test_data = encode_data(testing_data)
test_data
[[0, 3, 0],
[2, 4, 0],
[1, 2, 1],
[1, 1, 1],
[2, 3, 2],
[1, 2, 0],
[2, 4, 0],
[0, 5, 1],
[2, 1, 1],
[0, 3, 2]]
for row in test_data:
print(row[-1],classify(row, test))
0 (array([0]), array([1]))
0 (array([0, 2]), array([1, 1]))
1 (array([1]), array([2]))
1 (array([1]), array([2]))
2 (array([0, 2]), array([1, 1]))
0 (array([1]), array([2]))
0 (array([0, 2]), array([1, 1]))
1 (array([0]), array([1]))
1 (array([1]), array([2]))
2 (array([0]), array([1]))
import pandas as pd
train = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
test = pd.read_csv('test.csv')
# train.head()
train_data = train.values.tolist()
train_data[0]
# train_data[0][0]
[1,
0,
3,
'Braund, Mr. Owen Harris',
'male',
22.0,
1,
0,
'A/5 21171',
7.25,
nan,
'S']